Foreword Introduction to OWASP
OWASP's full name is Open Web Application Security Project, a non-commercial organization dedicated to promoting the security of web application systems. Recently, the website published a report on the top 10 web application system security risks in 2021 (OWASP Top 10), which will be listed every few years. Since its first release in 2003, the annual ranking of information security vulnerability attacks has gradually become a reference standard in the market, and also provides some cases, impact factors and preventive measures.
Top 10 Website Security Updates for 2021
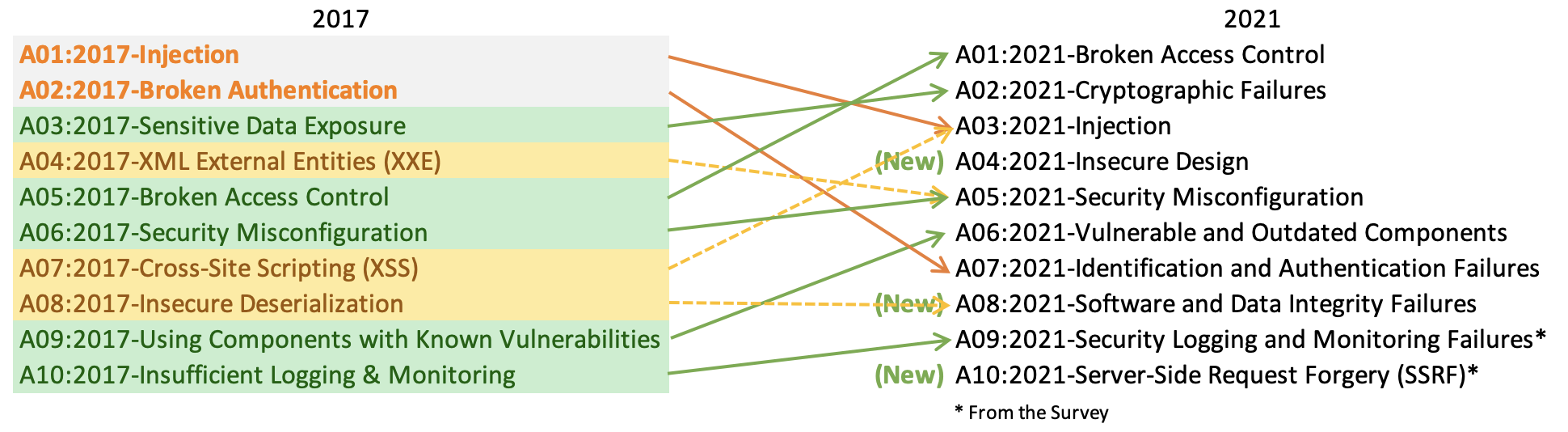
From the 2017 ranking to this year 2021, it can be seenBroken Access ControlFrom fifth place to first place, three other newly added risks are:Insecure Design,Software and Data Integrity Failures,Server-Side Request Forgery.
TOP10 ranking table
A01:2021-Broken Access Control
A02:2021-Cryptographic Failures
A03:2021-Injection
A04:2021 - Insecure Design
A05:2021 - Security Misconfiguration
A06:2021 - Vulnerable and Outdated Components
A07:2021-Identification and Authentication Failures
A08:2021-Software and Data Integrity Failures
A09:2021 - Security Logging and Monitoring Failures *
A10: 2021-Server-Side Request Forgery *
1st place Broken Access Control
Permission control failure, moved up from the fifth place; 94% tested applications have detected a certain type of permission control failure problem. The 34 CWEs corresponding to the category of access control failure appear more frequently in the test data than other vulnerability categories.
2nd place Cryptographic Failures
Encryption failure, promotion from 1st to 2nd place, was previously exposed as sensitive data, which is more akin to a broad problem than a root cause by this definition. Here we redefine and define the core of the problem as the failure of the encryption mechanism, resulting in the leakage of sensitive data or the destruction of the system.
3rd place Injection
Injection attack, slipped to third place. 94% All tested applications have problems with some type of injection attack. The 33 CWEs mapped in the injection attack category had the second highest number of occurrences in the test data for vulnerability issues. Cross-site scripting attacks now fall into this category in the new version.
Fourth place Insecure Design
Unsafe Design, this is a new category for the 2021 release, and focuses specifically on design-related deficiencies. If we really want to "shift the industry to the left" *Note 1*, then we must move further towards threat modeling, the concept of security design modules, and security reference architectures.
*Note 1: Move Left in the original English text means to identify and deal with related problems at an early stage in the software development and delivery process, which is the same as Shift Left Testing. *
Fifth place Security Misconfiguration
Security setting flaws, moved up from sixth place in the previous version. 90% All tested applications were detected with some type of security configuration flaw. As more software moves towards higher and more resilient settings, we are not surprised that this category of issues moves up. XML External Entities attacks in previous versions now fall into this category.
6th Vulnerable and Outdated Components
Dangerous or outdated components, previously titled Use components with known weaknesses. Ranked second in the industry survey in this edition, but has enough statistics to make it into the Top 10. This category climbed from ninth to sixth in the 2017 edition, and it's one that we continue to struggle with testing and assessing risk. This is also the only category where no CVEs can be mapped into CWEs, so the default threat and impact weights are preset to 5.0 on this category's score.
No. 7 Identification and Authentication Failures
Authentication and verification mechanisms failed, previously titled Bad Authentication Mechanism. In this edition, oil slipped to second place, and also included the CWE that was missing certification. This category is still an integral part of the Top 10, but it has also been found that the now standardized architecture can help reduce the chance of sub-risks.
No. 8 Software and Data Integrity Failures
Software and Data Integrity Failures, a brand new category for the 2021 release, and not presupposed and evaluated for integrity validation in software updates, alert and critical data, and CI/CD pipelines. The CVE/CVSS profiles with the highest impact weights in the assessment correspond to the 10 CWEs in this category. Insecure deserialization from the 2017 release is now merged into this category.
No. 9 Security Logging and Monitoring Failures
The failure of information security records and monitoring was previously incomplete records and monitoring and was included in the industry questionnaire. This time it ranked third and moved up from the previous tenth. This category will be expanded to include more relevant deficiencies, but this is also quite difficult to verify, and there is not quite a lot of CVE/CVSS data to support it. But the absence of this category directly affects overall security visibility, event alerting and forensics.
10th Server-Side Request Forgery
Server-side request forgery, a category that was ranked #1 in the industry survey, is included in this release. The data shows that this question has a lower number of tests and scope, but an above-average threat and impact weight ratio. This category also arises because industry experts have repeatedly stated that this category of issues is very important, even though there is not enough information to show this issue in this document.




